RedN NAWQA
USGS IN YOUR STATE
USGS Water Science Centers are located in each state.
|
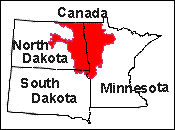
Red River of the North Basin
National Water-Quality Assessment Program
Cowdery, T.K., Stoner, J.D., Lorenz, D.L., 1995, Distribution and Movement
of Nitrate in a Surficial Outwash Aquifer Beneath Irrigated Copland,
Nowrthwestern Minnesota: American Geophysical Union, EOS Transactions,
Abstracts for Fall Meeting -- December 11-15, 1995, p. 186.
Abstract
A 6-kilometer section of sand and gravel aquifer along an approximate line of
ground-water flow was studied to determine the distribution and movement of
nitrate from a recharge area to a gaining stream. The area is predominantly
irrigated cropland where about 72 percent of nitrogen application is
commercial fertilizer. A statistically random sampling of ground water from a
100 square kilometer area of the surficial aquifer was done in 1994. Nitrate
concentrations near the water table ranged from below laboratory detection
(0.5 milligrams per liter as nitrogen (mg/L)) to 43 mg/L. Nitrate
concentrations exceeded 10 mg/L in 37 percent and 3.0 mg/L in 63 percent of the samples. The median nitrate concentration was 5.6 mg/L, large enough to indicate enrichment of ground water with nitrate from fertilizer applications. Analysis of water sampled in 1994 from wells and well clusters along the flow transect however, showed a large range in nitrate concentration (below detection to 12 mg/L) near the water table and a generally small range in concentration (from below detection to 0.56 mg/L) near the bottom of the 15-meter-thick aquifer. Spatial variability of nitrate concentration in ground water near the water table was fairly constant throughout 1994 and 1995 and suggests that loading of nitrate to the water was from fertilized, irrigated fields. Vertical variability of nitrate concentration in the aquifer was analyzed by age dating of ground-water samples from the flow transect and by numerical simulation of steady-state advective flow through the aquifer-stream system. Based on these analyses, the distribution of nitrate concentration with depth in the aquifer more likely is affected by the history of nitrogen application at land surface over the past 50 years and the presence of discontinuous clay layers within the aquifer rather than by transformation of nitrate to other nitrogen forms such as ammonium.
|