RedN NAWQA
USGS IN YOUR STATE
USGS Water Science Centers are located in each state.
|
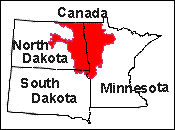
Red River of the North Basin
National Water-Quality Assessment Program
Cowdery, T.K., 1994, Nutrient Concentrations Near the Water Table of the Sheyenne
Delta Aquifer Beneath Cropland Areas--Preliminary Results from a Red River of the
North Basin Land-Use Study: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 94-397,
Proceedings Abstracts, American Water Resources Association 30th Annual
Conference, Symposium on National Water Quality Assessment (NAWQA) Program
-- November 7-9, 1994, Chicago, Illinois, p. 7.
Abstract
The U.S. Geological Survey is studying the effects of agriculture on water quality in the Sheyenne Delta aquifer in southeastern North Dakota. This study is part of a larger effort to evaluate ground-water quality in shallow aquifers within the Red River of the North Basin as part of the National Water-Quality Assessment program. The aquifer is a near-shore deltaic-facies deposit composed of interbedded fine to medium sands and silts up to 37 meters thick. The main agricultural commodities produced in the area are corn and sunflowers. Lesser amounts of soybeans, small grains, potatoes, and cattle forage are also produced. These crops are commonly irrigated with water from the surficial aquifer. The high rains during the early part of the 1993 growing season raised the water table to within one half meter of the land surface in many areas. Historical nitrate concentrations in ground water from the aquifer range from less than 0.23 to 3.68 milligrams per liter nitrate as nitrogen. After the 1993 recharge, these concentrations ranged from less than 0.05 to 4.30 milligrams per liter nitrate as nitrogen. These data suggest that this intense recharge substantially diluted the concentration of nitrogen from agricultural activity in the area.
|