Minnesota Water Science Center
UMIS NAWQAUSGS IN YOUR STATEUSGS Water Science Centers are located in each state. 
|
Agricultural Synoptic Study Design and ObjectivesObjective: Determine how water-quality indicators (nutrient concentration, herbicide concentration, suspended sediment concentration, biological condition, and primary productivity) differ in response to changes in riparian cover and soil conditions in streams in high-intensity corn and soybean rowcrop areas. Background: 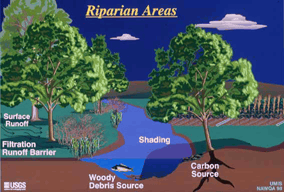 Intensive agriculture can alter water quality and aquatic communities in streams in the Upper Midwest through nutrient and organic enrichment, increased turbidity due to acceleration of erosion and sedimentation, increased light penetration and water temperature due to removal of wooded riparian Cover. Stream basin alterations may contribute to the excessive growth of aquatic vegetation, reduced species richness and community diversity, and shifts in community composition. and increased algal productivity. Soil characteristics of stream basins influence the delivery of water, nutrients and sediments entering streams. Soils delivered to streams from agricultural fields affect biological communities by reducing light availability and habitat (and by increasing the availability of contaminants associated with suspended sediments. Wooded riparian buffer strips between agricultural fields and streams may provide a barrier that reduces nutrient and sediment inflows and provides canopy shading and instream
habitat sources.
Intensive agriculture can alter water quality and aquatic communities in streams in the Upper Midwest through nutrient and organic enrichment, increased turbidity due to acceleration of erosion and sedimentation, increased light penetration and water temperature due to removal of wooded riparian Cover. Stream basin alterations may contribute to the excessive growth of aquatic vegetation, reduced species richness and community diversity, and shifts in community composition. and increased algal productivity. Soil characteristics of stream basins influence the delivery of water, nutrients and sediments entering streams. Soils delivered to streams from agricultural fields affect biological communities by reducing light availability and habitat (and by increasing the availability of contaminants associated with suspended sediments. Wooded riparian buffer strips between agricultural fields and streams may provide a barrier that reduces nutrient and sediment inflows and provides canopy shading and instream
habitat sources.Approach: Twenty-four sites in the Minnesota River Basin were selected as part of a comprehensive study conducted in the UMIS, Eastern Iowa Basins, and the Lower Illinois Basin NAWQA study units. Streams with greater than 50 percent agricultural land and with drainage areas ranging from 100 to 1000 square miles were considered for sampling. Twenty-four sites which met these criteria were then divided into four categories based on riparian cover and soil conditions: 1. Good riparian cover, moderately well drained soils 2. Good riparian cover, poorly drained soils 3. Poor riparian cover, moderately well drained soils 4. Poor riparian cover, poorly drained soils During August 1997, water sampling, discharge measurments, fish and invertebrate collections, and habitat characterizations were accomplished. Major Findings: For results in the UMIS Study Unit click here. For a broader context of the effects of riparian zones on the quality of Midwestern streams click here. Publications: Lee, K.E., Fallon, J.D., and Hanson, P.E., 1998, Effects of wooded riparian zones and soil runoff potential on metolachlor, acetochlor, and alachlor herbicides and their ethane-sulfonic metabolites [abs.]: North American Lake Management Society 18th International Symposium, November 10-13, 1998, Banff, Alberta, Canada, p. 114. Lee, K.E., Goldstein, R.M., and Hanson, P.E., 2001, Relation between fish communities and riparian zone conditions at two spatial scales: Journal of the American Water Resources Association, v. 37, no.6, p. 1465-73. Lee, K.E., Stauffer, J.C., Hanson, P.E., and Goldstein, R.M., 1997, Expected effects of wooded riparian cover and soil conditions on water quality in southeastern Minnesota [abs.]: 59th Midwest Fish and Wildlife Conference, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, December 7-10, 1997, p. 420. Stark, J.R, Fallon, J.D., Fong, A.L., Goldstein, R.M., Hanson, P.E., Kroening, S.E., and Lee, K.E., 1999, Water-quality assessment of part of the Upper Mississippi River Basin, Minnesota and Wisconsin--Design and implementation of water-quality studies, 1995-98: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4135, 85 p. Stark, J.R., Hanson, P. E., Goldstein, R.M., Fallon, J.D., Fong, A.L., Lee, K.E., Kroening, S.E., and Andrews, W.J., 2001, Water quality in the Upper Mississippi River Basin, Minnesota and Wisconsin, South Dakota, Iowa, and North Dakota, 1995-98: U.S. Geological Survey Summary Circular 1211, 35 p. Stauffer, J.C., and Goldstein, R.M., 1998, Relation of wooded riparian zones and soil runoff potential to fish assemblage composition in the agricultural Minnesota River Basin [abs.]: American Fisheries Society, 128th Annual Meeting, August 23-27, 1998, Hartford, Connecticut, p. 178. Stauffer, J.C., Goldstein, R.M., and Newman, R.M., 2000, Relationship of wooded riparian zones and runoff potential to fish community composition in agricultural streams: Canadian Journal of Aquatic Science, v. 57, p. 307-316. ZumBerge, J.R., Perry, J.A., and Lee, K.E., 2003, Influence of local riparian cover and watershed runoff potential on invertebrate communities in agricultural streams in the Minnesota River Basin: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 03-4068, 13 p. |